Understanding the enteric nervous system and its impact on health
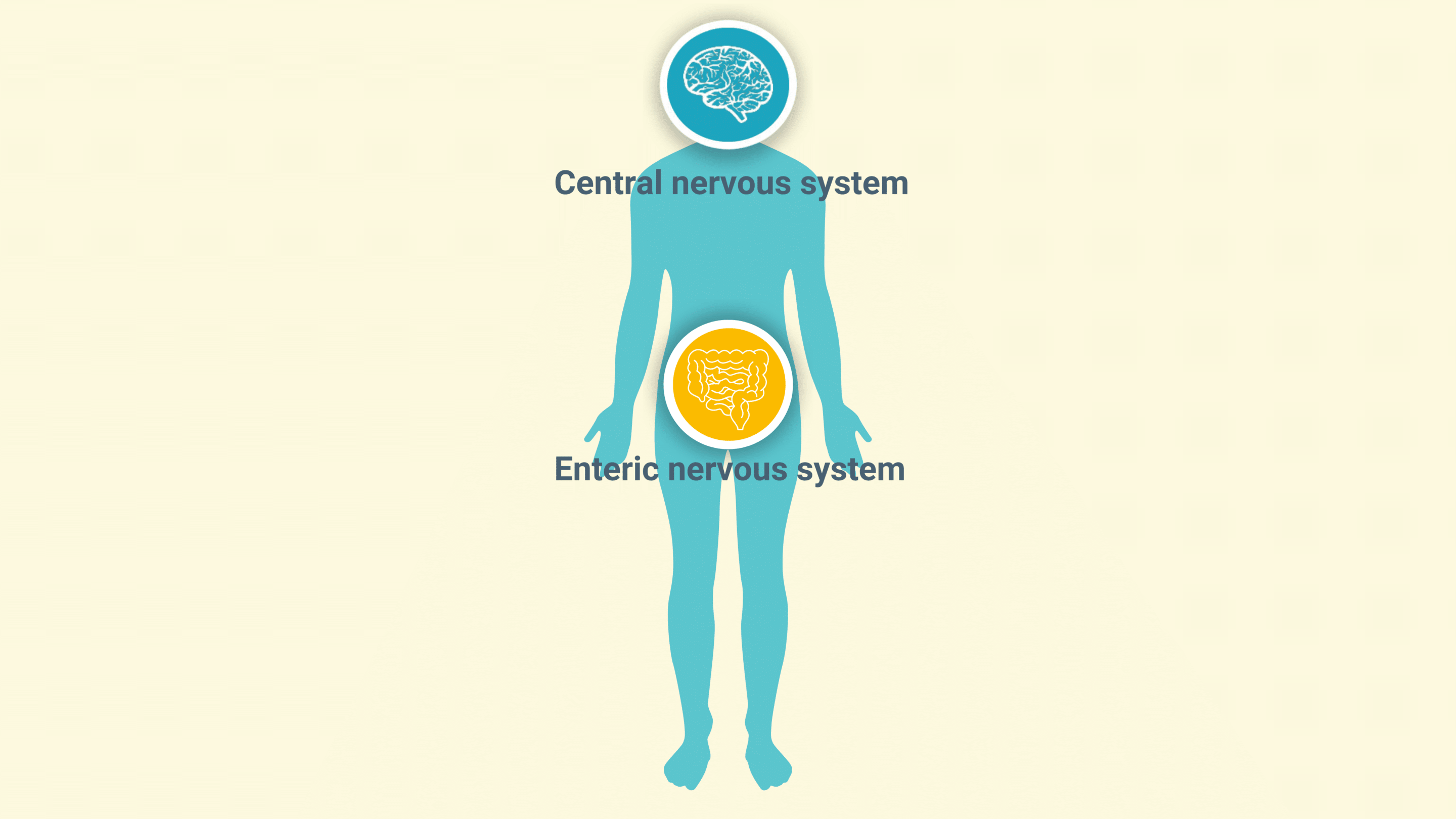
The enteric nervous system (ENS), often referred to as the “second brain”, is a vast network of neurons embedded in the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. It plays a critical role in regulating digestion, nutrient absorption, and even systemic glucose metabolism. Far from being a simple controller of gut motility, the second brain also communicate with the central nervous system via the gut-brain axis, influencing overall metabolic health and homeostasis. Emerging research suggests that targeting enteric nervous system function could offer new therapeutic avenues for managing metabolic disorders, including type 2 diabetes (T2D).
In diabetic conditions, alterations in enteric nervous system function can lead to duodenal hypercontractility, increased glucose absorption, and impaired gut-brain communication, all of which contribute to insulin resistance. While many therapies focus on peripheral glucose regulation, targeting the ENS directly offers an innovative approach to addressing the root causes of metabolic dysfunction.
In this context, Enterosys conducted a study exploring the effects of galanin, a neuropeptide, on the enteric nervous system neurons. The study aimed to determine whether galanin could modulate ENS activity, improve gut-brain axis communication, and ultimately enhance glucose metabolism in diabetic mice.
Enterosys explores galanin’s effect on the second brain
To investigate the impact of galanin on the enteric nervous system function, we utilized a preclinical mouse model of diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. The experimental protocol involved both ex vivo and in vivo approaches to measure the effects of oral galanin administration on duodenal contractions, nitric oxide (NO) release from ENS neurons, hypothalamic NO levels, and glucose metabolism.
In ex vivo experiments, isolated duodenal tissues were treated with galanin, and contractions were measured using isotonic transducers. Additionally, real-time NO release from enteric nervous system neurons was monitored using amperometric sensors. To understand how these local gut changes translate into systemic effects, hypothalamic NO release and glucose uptake in key metabolic tissues—such as liver, muscle, and adipose tissue—were also measured following galanin treatment.
In vivo, diabetic mice were subjected to chronic oral gavage with galanin over one week. Changes in blood glucose levels, insulin sensitivity, and glucose tolerance were assessed through oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT) and HOMA-IR calculations. Tissue samples were analyzed for gene expression and protein activity associated with glucose metabolism and insulin signaling.
This multi-faceted approach allowed us to capture both the local effects of galanin on the second brain and its broader systemic implications on glucose homeostasis.
Galanin’s impact on enteric nervous system and glucose metabolism
The findings from Enterosys revealed significant effects of galanin on enteric nervous system function and systemic glucose metabolism. Galanin was shown to stimulate nitric oxide (NO) release from the second brain, specifically those expressing neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase (nNOS). This NO release led to reduced duodenal contractions, effectively slowing down glucose absorption in the small intestine. These effects were blocked by galantide, a galanin receptor antagonist, confirming that galanin’s actions are receptor-mediated .
Beyond local gut effects, galanin treatment also modulated hypothalamic NO release, a critical factor in gut-brain communication. The increase in hypothalamic NO levels triggered improved glucose uptake in key metabolic tissues, including the liver, skeletal muscle, and subcutaneous adipose tissue. Interestingly, glucose uptake occurred without significant glycogen storage, suggesting direct utilization of glucose for energy rather than storage .
In diabetic mice, chronic oral administration of galanin significantly improved insulin sensitivity, reduced fasting blood glucose levels, and enhanced overall glucose tolerance. The HOMA-IR index, a marker of insulin resistance, showed substantial improvement after galanin treatment. These effects were accompanied by enhanced AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) signaling in skeletal muscle, further supporting the role of galanin in improving cellular glucose utilization .
These results suggest that galanin acts as a potent modulator of enteric nervous system function, not only by reducing duodenal hypercontractility but also by restoring gut-brain communication and enhancing peripheral glucose metabolism.
Partner with enterosys for advanced research
At Enterosys, we combine scientific expertise with innovative methodologies to deliver cutting-edge insights into gut-organ interactions, including the enteric nervous system function. Our preclinical studies, such as the investigation of galanin, demonstrate our commitment to driving impactful discoveries in metabolic health. Contact us today to valorise your compound !
Source :
Abot A, Lucas A, Bautzova T, Bessac A, Fournel A, Le-Gonidec S, Valet P, Moro C, Cani PD, Knauf C. Galanin enhances systemic glucose metabolism through enteric Nitric Oxide Synthase-expressed neurons. Mol Metab. 2018 Apr;10:100-108. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.01.020. Epub 2018 Jan 31. PMID: 29428595; PMCID: PMC5985240.